 Hearing tests can be subjective (where the client responds when they hear the sound during testing) or objective tests (where the client does not indicate they have heard the sound). For example, electrophysiological tests look at how different parts of the hearing mechanism function, such as Auditory Brainstem Testing (ABR), Auditory Cortical Testing (ACR), Oto-acoustic Emissions (OAEs) and Electrocochleography (ECochG). These tests require special training to carry out and special skills to interpret the results.
Hearing tests can be subjective (where the client responds when they hear the sound during testing) or objective tests (where the client does not indicate they have heard the sound). For example, electrophysiological tests look at how different parts of the hearing mechanism function, such as Auditory Brainstem Testing (ABR), Auditory Cortical Testing (ACR), Oto-acoustic Emissions (OAEs) and Electrocochleography (ECochG). These tests require special training to carry out and special skills to interpret the results.
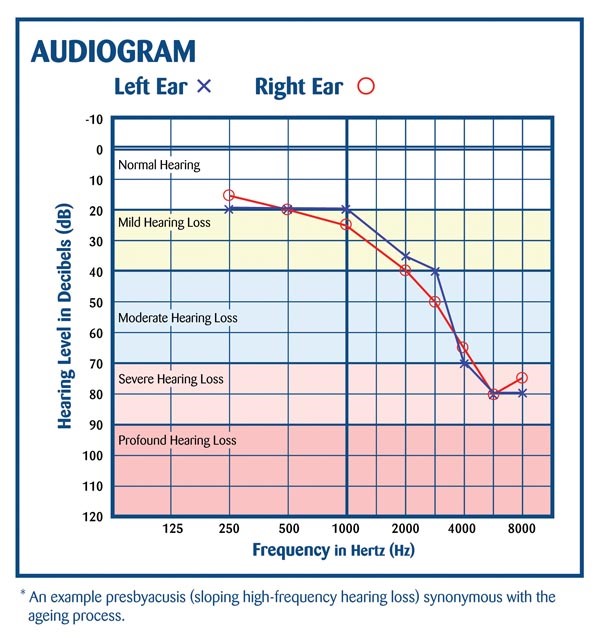
Pure Tone Audiometry
Pure tone audiometry is the most common type of hearing test. It can be used for clients from about 3 years of age. Pure tone audiometry measures thresholds for pure tone sounds, usually while you are in a sound booth. An Audiometer is used to present tones of varying pitch and loudness. The test signals are usually presented through calibrated headphones and a bone conductor. You will be asked to respond each time you hear the tone; by pressing a response button, raising your hand or by tapping on the desk. Your measured responses are charted on a graph called a pure tone audiogram. These results determine if a hearing loss exists, the nature of any hearing loss detected and the severity.
Impedance Audiometry
Impedance tympanometry measures the mechanical function of the middle ear system. This includes the mobility and elasticity of the eardrum, the status of the middle ear cavity and bones. A small probe is placed in the ear canal attached to a soft tip to create a pressure seal and elicit a gentle probe tone. Abnormalities of pressure and movement can be detected with this test. This procedure is non invasive and does not involve any physical contact with the eardrum.
 Impedance Acoustic Reflex Testing
Impedance Acoustic Reflex Testing
Impedance acoustic reflexes, otherwise known as Stapedial Reflexes, form part of the impedance audiometry test battery. They are completed for each ear in conjunction with tympanometry. Acoustic reflex testing is valuable in interpreting results from other audiometry tests. It is also an important test in detecting problems in the auditory pathway beyond the level of the inner ear.
Speech Audiometry
Speech audiometry is used to determine your ability to discriminate the spoken word; usually performed in quiet. Occasionally speech audiometry will be performed in the presence of background noise to determine how much difficulty challenging environments pose to the individual. The results of speech discrimination testing enable our Audiologist to consider further assessments if needed.
Otoacoustic Emissions (OAEs)
This procedure measures a facet of hearing cell activity in the organ of hearing, which can be used to predict degree of hearing loss and other potential issues of hearing integrity. A small probe in positioned in the ear canal, to conduct the stimulus to the ear and record the response (cochlear echo). Otoacoustic emissions are very sensitive to hearing loss and are used extensively in newborn hearing screening programs as a quick, safe and efficient means of detecting loss. They have considerable value also in monitoring the effects of ototoxic medications due to their sensitivity to hair cell damage within the cochlea.
City Hearing’s audiologists are qualified to perform all the above tests. Patients may self-refer or attend upon referral from their GP or relevant health provider. Medicare rebates are applicable with a written referral from a GP(Chronic Disease Management Program), ENT Specialist or Neurologist.

